Even in the weird universe of minor cannabinoids, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) stands out. It’s the most (or second-most) abundant compound in most marijuana plants, but if you try to vape or smoke it, it disappears before the vapor reaches your lips. And, while it’s the direct precursor to highly psychoactive delta 9 THC, THCA by itself is not intoxicating.
The reason it disappears when you vape or smoke it is that THCA is extremely volatile and instantly converts into delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (delta 9 THC) with exposure to heat (and converts more slowly with exposure to oxygen).
THCA is the acidic precursor to delta 9 THC, but other cannabinoids in hemp and marijuana plants also have acidic forms too—most notably, cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) and cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), the precursors to CBD and CBG. Which cannabinoid is most abundant varies depending on the cannabis strain.
THCA carts and disposables are slightly more controversial than other hemp-derived cannabis products. This inactive cannabinoid is closely linked to THC, but their properties and uses overlap less than you’d expect.
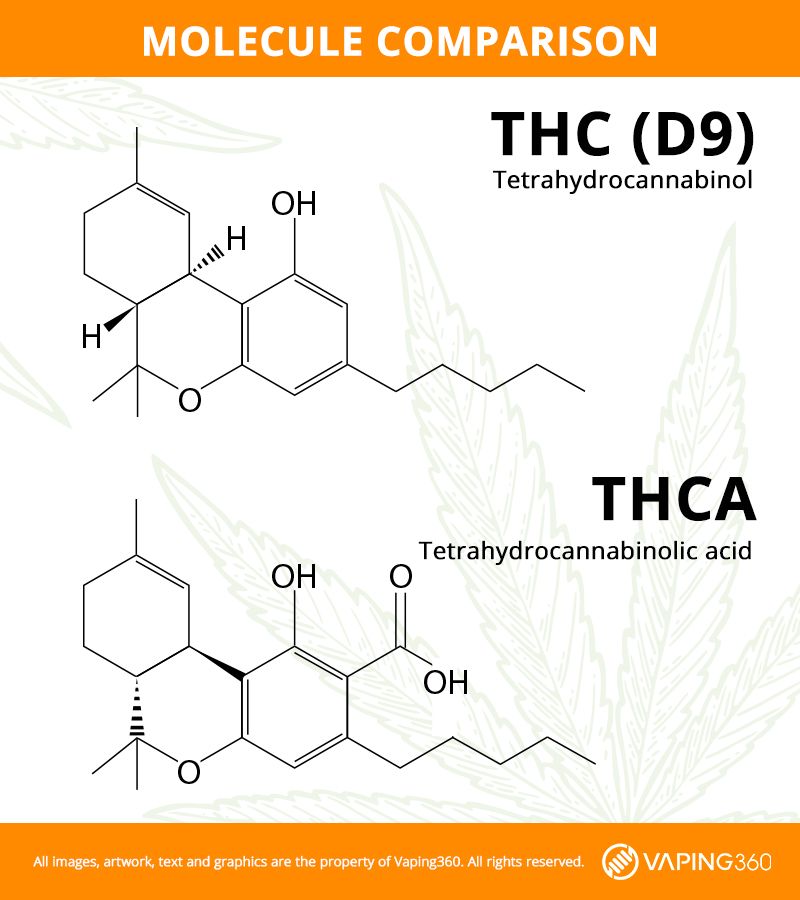
What are the differences between THCA and THC?
Chemical structure
THCA and delta 9 THC have relatively similar makeups, minus one key feature: a carboxylic acid group in THCA. Delta 9 THC is a non-acidic substance with a lower molecular weight.
Because its carboxyl group is easily shed with heat, oxygen, or age, THCA is far less stable than THC and many other cannabis compounds. It only takes temperatures in excess of 230° F (110° C) to decarboxylate (i.e. strip a carboxyl group from) THCA molecules. Higher heat is required to extract essential benefits from oils or bud.
Also of note, THC weighs 87.7% as much as THCA. Since THCA is heavier than delta 9 THC, it doesn’t convert into an equivalent amount after shedding its carboxylic acid group. A product with 5 mg of THCA will contain about 4.4 mg of delta 9 after it’s heated and decarboxylated (plus any THC that was already available).
Psychoactivity
One of the primary distinctions between THC and THCA is their ability to get you high. Or inability, in the case of THCA.
Delta 9 THC has a high binding affinity for the body’s CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors. When THC molecules bind to those receptors, they trigger a surge of dopamine and strong feelings of euphoria. That’s the THC high we know and love.
However, THCA molecules are too large to bind to CB1 and CB2 receptors. It still enters the bloodstream and interacts with the central nervous system, but it won’t get you high. The only way to get high from THCA is by decarboxylating it, either through vaping, smoking, or heating it manually in an oven—or waiting a long time for oxygen and light to do the job. Even after these efforts, you aren’t getting high from THCA itself. You’re now consuming delta 9 THC.
Therapeutic effects
Let’s clarify: we’re talking now about raw, inactive THCA. Consuming vape carts or disposables with converted THCA won’t offer its potential benefits.
Over the past few years, especially, THCA has been at the center of a few promising studies:
- Neuroprotection: It’s possible that THCA, along with its cousin CBDA, has neuroprotective qualities. Unprocessed THCA may be a useful addition to Alzheimer’s or dementia care in the future.
- Anti-inflammation: Research suggests that THCA may have significant anti-inflammatory properties, and it could offer relief from irritable bowel disease (IBD) symptoms.
Delta 9 THC has undergone more research than THCA, and shows promise as a treatment for many conditions. The possible benefits of delta 9 THC include:
- Anti-inflammation: Delta 9 THC may downregulate inflammatory responses, including those associated with respiratory distress and contact dermatitis.
- Pain reduction: THC appears to reduce certain kinds of chronic pain, including neuropathic pain; these benefits may be amplified when delta 9 is administered along with CBD.
- Antiemetic: Results have been mixed over the years, but several studies indicate that THC could reduce nausea.
- Neuroprotection: As an antioxidant, THC appears to prevent glutamate-induced death of neurons.
In short, both THC and THCA seem to have anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties, just with separate applications. Some of THC’s medicinal effects, however, are unique.
Commercial availability
If you live in a legal marijuana state, delta 9 THC products are more accessible than THCA derived from hemp. You’ll also have a far wider variety to choose from: THC carts, disposable vapes, edibles, and tinctures.
Remember, delta 9 THC is far more chemically stable than THCA. Although THC can be destroyed or converted into CBN with poor storage, this is a slow process and won’t occur as you vape or smoke.
The conversion of THCA into delta 9 THC is rapid. By the time vapor hits your lungs, the THCA has already activated and transformed into THC. Production of truly THCA-rich hemp products is extremely challenging. Conversion will occur during most typical manufacturing processes, which use heat.
Generally, THCA products are available in bud, capsule, or tincture form. While the bud can be juiced, blended into smoothies, or sprinkled onto a salad, you must ingest it raw to reap any rewards unique to THCA. Vaping or smoking means you’re consuming standard bud—because the THCA turns to THC before you inhale it.
Legality
Some U.S. states are cracking down on THCA, but federally, it’s treated the same as other hemp derivatives under the 2018 Farm Bill. Double-check that your location doesn’t base its laws around total THC content rather than delta 9 levels alone.
Hemp products are legally required to contain under 0.3% delta 9 THC by dry weight. Any hemp bud, tinctures, or edibles containing THCA are tightly bound to this restriction. It’s easier for carts and disposable vapes to adhere to the THC limit since they usually contain other cannabinoids, too. Truly high-THCA hemp products take a good deal of care and patience to create without exceeding the delta 9 THC limit.
Marijuana (and delta 9 THC) is a Schedule I controlled substance in the United States. You can only purchase legal delta 9 products if you live in a state that explicitly permits them.
How are THC and THCA similar?
Most similarities between delta 9 THC and THCA relate to origin. Both are phytocannabinoids—compounds found naturally in the cannabis plant. Some other properties shared by the two cannabinoids include:
- Byproducts of CBGA: Acidic CBGA—sometimes called the mother cannabinoid—is a precursor to both THC and THCA. The fate of CBGA comes down to the enzymes it interacts with. If transformed by THCA synthase, it becomes THCA; that same THCA is later converted into delta 9 THC.
- Nervous system interactions: Both THC and THCA penetrate the blood-brain barrier after consumption. And despite differences in behavior and binding, both interact with the central nervous system.
- Medicinal potential: Delta 9 THC and THCA may be useful in certain areas of medicine, including anti-inflammatory treatments. More research is needed to confirm the effects.
Additionally, both cannabinoids are composed of hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon. THCA simply has an extra carboxyl group.
Which is better: THCA or THC?
Neither THCA nor THC are superior. As these cannabinoids have such different effects and uses, it all depends on what you’re looking for: THC to get high and THCA if you’re interested in its potential therapeutic properties. Just remember that research is in its early stages, and little about THCA has been confirmed.
High-THCA bud and certain THCA carts are handy if you live in a region without legal marijuana. Just check the COA to confirm safety and THCA content, as well as the presence of other cannabis oils.
FAQ: Delta 9 THC vs. THCA
Does THCA get you higher than delta 9?
No, the vast majority of delta 9 THC products will get you higher than THCA hemp, even if the raw marijuana contains barely over 0.3% THC.
As true THCA hemp products are difficult to produce, it’s more likely that the THCA product you’re using is actually a blend of several extracts. Numerous “THCA” carts are packed with delta 8 THC oil and garnished with a dash of THCA. Although THCA becomes delta 9 THC with heat, delta 8 is not a precursor and won’t convert into something more potent.
Delta 8 THC is about half as psychoactive as delta 9 THC. Not only does this render THCA products weaker, but their strength varies widely. Marijuana products, no matter the strain, are highly regulated, and results are more consistent.
Is THCA safer than delta 9 THC?
Based on commercial regulations alone, THCA products are potentially less safe than those highest in THC.
Legal marijuana is subject to rigid production, quality, and testing standards. Hemp products are unregulated, so there are no safety or third-party testing requirements for sellers. It’s up to the buyer to investigate the product before using it.
Only buy THCA hemp from trusted retailers with transparent safety testing. Third-party testing ensures that the product contains the listed ingredients in the correct amounts. Don’t rely on packaging, either; many sellers make misleading claims about THCA hemp products, and certificates of analysis (COAs) could contradict marketing.
Is THCA flower the same as marijuana bud?
Unlike other kinds of hemp bud, THCA bud is rarely infused. It instead contains higher than average quantities of THCA at the time of testing and lower quantities of converted THC than similar marijuana plants. The only way to achieve this is through selective breeding in a temperature-controlled environment (so the THCA doesn’t convert to THC).
There are similarities between high-THCA hemp flower and marijuana, but the latter is more potent. Inactive marijuana often contains between 0.5% and 2% THC, plus a generous helping of THCA.
President Trump promised during his election campaign to “save vaping," but his administration has undermined that goal at every turn.
The U.S. disposable vape market has grown to $2 billion in annual sales, although nearly none of the products are authorized by the FDA.
More than 30 bills that would impose severe restrictions vaping consumers’ product choices remain active in U.S. state legislatures.
The Freemax REXA PRO and REXA SMART are highly advanced pod vapes, offering seemingly endless features, beautiful touchscreens, and new DUOMAX pods.
The OXVA XLIM Pro 2 DNA is powered by a custom-made Evolv DNA chipset, offering a Replay function and dry hit protection. Read our review to find out more.
The SKE Bar is a 2 mL replaceable pod vape with a 500 mAh battery, a 1.2-ohm mesh coil, and 35 flavors to choose from in 2% nicotine.




















![Image for What Is THC-JD? Legality, Effects, Potency Explored [Update]](https://media.vaping360.com/images/what-is-thc-jd-thumbnail-20a40b517a.webp?imageType=Standard)
