THC-O, the acetate ester form of THC, had a brief moment in the spotlight as a competitor to delta 8 THC and HHC, among other hemp-derived market competitors. But the discovery that heating an acetate compound like THC-O creates dangerous ketene gas made the cannabinoid risky to sell (and use!).
Acylating THCP, possibly one of the strongest cannabinoids in existence, was an obvious next move—but not necessarily the wisest. Heating and inhaling any acetate ester can seriously damage the lungs—and that includes THCP-O and HHC-O. If you want to try these novel acetate cannabinoids, use only edibles or tinctures. Never vape or smoke acetates. (For more info, check the note at the top of our THC-O article.)
Hemp-derived cannabis products have become increasingly potent. Delta 8 THC was a modest start, but standards are shifting as the industry matures and users gain a clearer sense of what’s possible. Where does THCP-O fit in?
What is THCP-O?
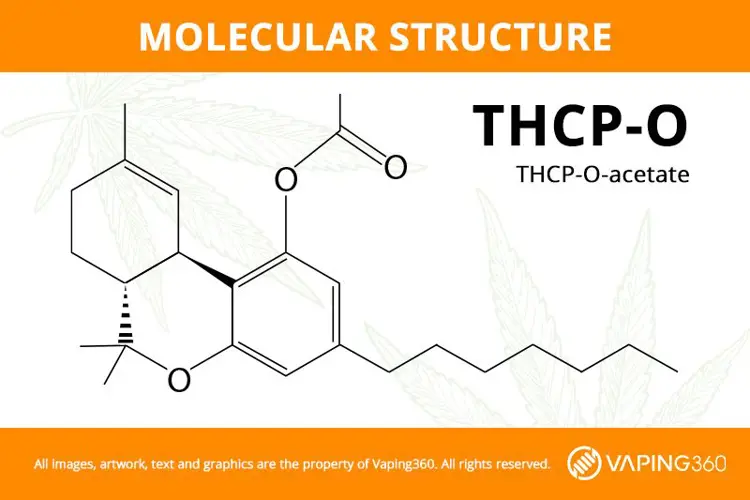
Tetrahydrocannabiphorol acetate (THCP-O-acetate or THCP-O) is the acetate ester form of THCP, a potent cannabinoid that caught the eye of hemp researchers back in 2019. THCP is famous for its seemingly unmatched binding affinity with the CB1 receptor.
CB1 receptors are found throughout the human endocannabinoid system (ECS), particularly in the brain and spinal cord. The more readily a substance binds to these nervous system hotspots, the more likely it is to get you high.
Identifying THCP as psychotropic was the easy part. From there, it’s been a matter of exploring the intensity of the THCP high, and the effects it creates when consumed by actual users. Research is scant, though compared to THCP-O, THCP isn’t too poorly documented.
Everything we know about THCP-O comes from anecdotes, claims by prospective sellers, and speculation.
Structurally, THCP-O merges the key features of THCP with those of acetate cannabinoids like THC-O and HHC-O. It shares the THCP molecule’s massive seven-carbon side chain (two atoms more than delta 9 THC’s chain), but unlike THCP, THCP-O has an acetate group.
There’s no evidence that THCP-O forms naturally in cannabis. Without intervention in a lab, it’s unlikely that this cannabinoid would see the light of day.
Does THCP-O get you high?
THCP-O will absolutely get you high. What's less clear is how THCP-O’s potency compares to THCP and THC-O, or even other niche acetate esters like HHC-O.
Some cannabis sellers have reported that THCP is over thirty times as potent as delta 9 THC and, thus, can get its users thirty times as high. That’s not exactly correct.
Researchers suspect that THCP binds to CB1 receptors thirty times more effectively than delta 9. That might mean you’ll get thirty times higher—or it might mean you’ll get twice as high, or maybe not even that. We don't know exactly how the binding affinity translates into the strength of the high. It’s all just a guess. Anecdotally, however, users report that THCP is highly intoxicating.
Don’t let yourself get too wrapped up in claims about THCP-O’s potency. A few sources lump it in with THCP and say that it’s thirty times more potent than marijuana-derived delta 9 THC, but zero research supports the claim—just anecdotes and speculation.
What are the effects of THCP-O?
As it stands, claims about THCP-O's effects are more in line with THCP than THC-O. You won’t find the word “psychedelic” thrown around as much, but plenty claim that THCP-O is extremely potent due to its seven-atom side chain.
By the way, even THC-O may or may not be psychedelic. Opinions are split, but according to a 2023 poll, few users report having that experience. Don’t expect anything too trippy out of THCP-O, either.
THCP-O is psychotropic. That's evident in its structural crossover with THCP and THC-O, as well as user anecdotes. Its specific effects, including benefits and potential adverse responses, are unknown.
Just to be extra clear, never vape or smoke THCP-O, or any product that contains any amount of THCP-O.
If you consume it—in edible or tincture form—make sure to ease your way into the session. Start with a small dose, wait for the effects to settle in, then take more to taste.
Potent cannabinoids can elevate your risk of an adverse reaction. If you’re regularly dealing with bad highs, or have poor responses to alt cannabinoids in general, be especially wary of THCP-O. Not only are its effects hard to predict, but they could be much more intense than those of other hemp-derived cannabinoids.
Is THCP-O safe?
Whether THCP-O is safe to consume in edibles or oils is unclear, but it definitely is not safe to vape or smoke. Vapers should stay far away from acetates of any kind.
Cannabinoids in acetate form, like THC-O and CBD-O, are known to convert into ketene gas when exposed to temperatures over 644 °F (340 °C). The same thing happens with all acetate substances. The infamous “EVALI” lung injury outbreak in 2019 was caused by weed vapers inhaling ketene formed by black market THC carts diluted with vitamin E acetate.
Ketene is a dangerous lung toxicant, and you put yourself at risk by inhaling any amount of it, whether or not the consequences are instantly severe or noticeable.
Untested vape products are often packed with cheap fillers and additives. But in the case of THCP-O it is the primary active substance that could cause severe lung damage.
Without third-party testing and a certificate of analysis (COA), there’s no way to verify a product’s purity or lack of fillers. But even that’s not enough when it comes to acetates. Additive-free or not, acetate esters are risky and should be avoided in weed carts.
Stay away from acetates to minimize your risk of serious, permanent lung injury, even when the cannabinoid in question is hyped up by sellers. There are plenty of safer options on the market.
THCP-O vs. THCP
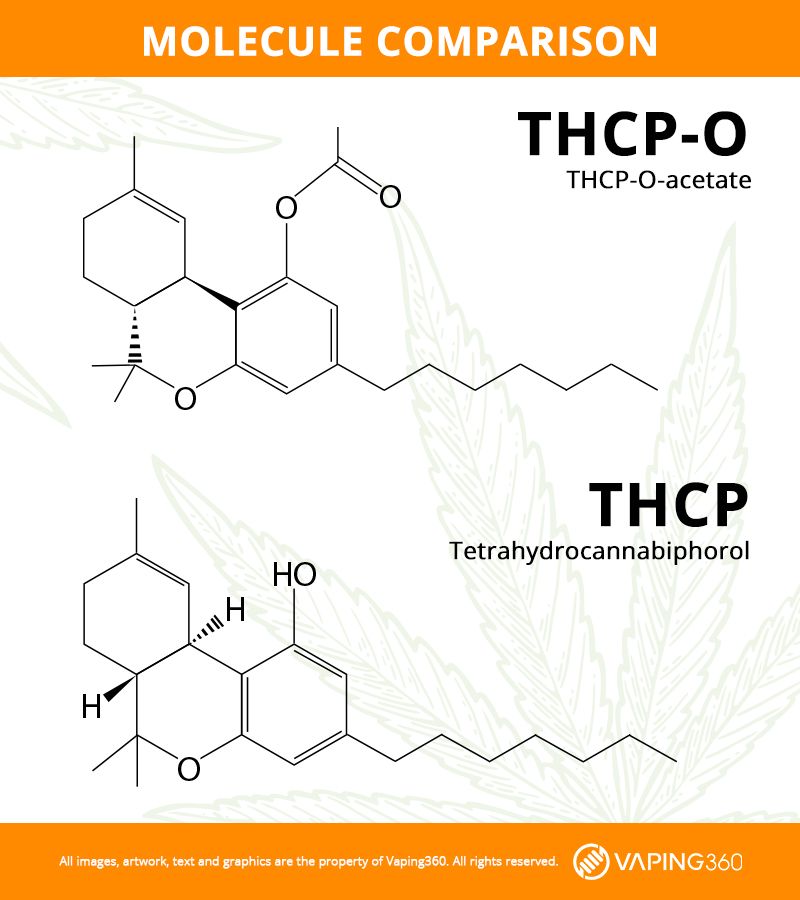
THCP-O and THCP are practically twins as far as structure goes. Take a THCP molecule, acylate its OH group, and you have THCP-O. Because of their similarity, it's possible that THCP-O and THCP produce equally intense highs.
Whether THCP-O is more akin to THC-O than THCP is a matter of interpretation, but the parallels are clear where they matter most: safety. You don’t need to worry about ketene gas if you’re vaping third-party tested THCP, but you do if you’re using THCP-O or THC-O.
There’s no evidence that THCP converts into a hazardous chemical when heated, and currently no reason to suspect that it does. It doesn’t have an acetate group.
We don’t know much about THCP, either. It’s so scarce in nature that researchers didn’t stumble across it until 2019. Even minor cannabinoids like delta 8 THC and HHC were identified in the mid-twentieth century, despite commercialization being a recent event.
As of June 2024, THCP-O hasn’t been isolated or found to be a natural constituent of cannabis.
Will THCP-O show up on a drug test?
We can’t say for sure, but it’s best to assume that THCP-O will show up on a drug test. Don’t try your luck if you have an upcoming screening.
Drug panels are complex when looking at novel hemp cannabinoids. Technically, these tests weren’t designed to pick up on substances like delta 8 THC and HHC. But they’re also seeking out metabolites—the byproducts of the liver breaking down a substance—rather than the cannabinoid itself.
Any cannabinoid that metabolizes into THC-COOH can trigger a positive screening. That’s exactly why you’ll hear tales about delta 8 users flunking drug tests: this legal hemp cannabinoid converts into the same secondary metabolite as delta 9 THC.
There's no research specific to THCP-O and drug testing. Information on its potential metabolites isn't available, either, which only makes the situation muddier. The best advice is to assume it will trigger a positive drug test result.
Is THCP-O legal?
Cannabinoids found naturally in hemp plants are federally legal under the 2018 Farm Bill. But since there’s no evidence that THCO-O is found naturally in hemp plants, it could be targeted by law enforcement, as happened with THC-O.











![Image for What Is THC-JD? Legality, Effects, Potency Explored [Update]](https://media.vaping360.com/images/what-is-thc-jd-thumbnail-20a40b517a.webp?imageType=Small)






