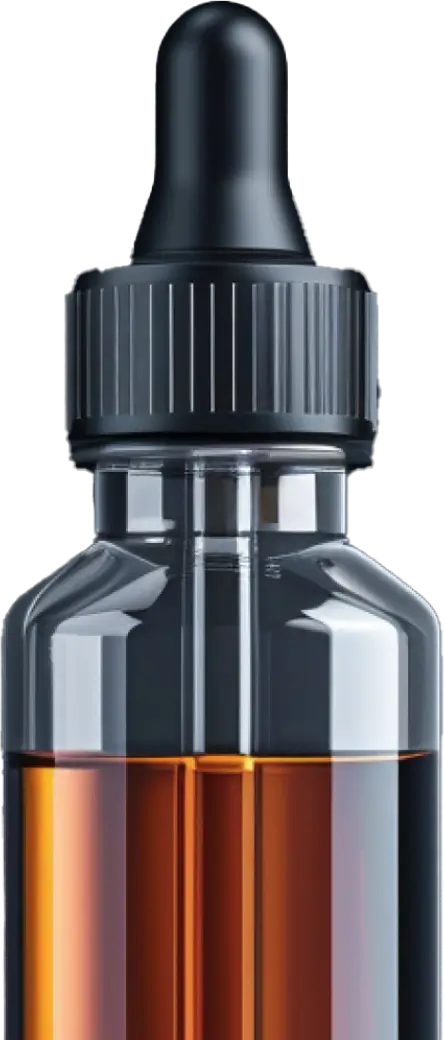
Cannabidiol, or CBD for short, is an organic compound that is found in the cannabis plant, with the flowers of the hemp plant being the richest source. And in order for CBD to be added to a wide array of consumer products—think CBD oil, lotions, topicals, or CBD vape juice—the first step that manufacturers need to take is to extract it from the plant.
This guide will present the various CBD extraction methods, essentially explaining how full-spectrum CBD oil is obtained from the CBD strains of cannabis. Some of these methods have been used in various industries for decades or even centuries, far before CBD oil was even a thing. Examples include essential oil extraction, decaffeination (and caffeine extraction) of coffee beans, and even beer production. In all cases, the idea is the same: how to extract a valuable resource out of plant material.
If you are interested in the ins and outs of CBD extraction from cannabis strains high in CBD, here's a breakdown of the most commonly used CBD methods.
Supercritical CO2 extraction
The word "supercritical" sounds real fancy, but it is actually a term that's very commonly used in chemistry. Simply put, a substance in its supercritical state possesses characteristics of both a gas and a liquid.
When supercritical CO2 is used in CBD extraction, its gas properties allow it to effuse through all plant matter, while its liquid properties allow it to extract compounds efficiently. The exact process varies, and some labs start the extraction with liquid CO2 while others start with CO2 in gas form. In both cases, manufacturers add CO2 in a chamber that includes plant material and use the exact amounts of pressure and temperature needed for CO2 to reach its supercritical state. At this point, and with the help of some additional heat, CO2 acts as a solvent and causes the plant material to separate, carrying with it all the essential compounds. Once done, CO2 is separated from the organic compounds, and manufacturers are left with full-spectrum CBD oil.
While it requires qualified personnel and there are higher costs associated with the equipment needed for supercritical CO2 extraction, it is by far the most efficient and quickest method to extract CBD. It is also environmentally friendly due to the limited amount of emissions, and safer than extractions that use certain solvents as CO2 is "generally regarded as safe" by the FDA.
Steam distillation
Steam distillation is a centuries-old process that’s commonly used to distill alcohol as well as extract essential oils from organics. The process is much less complicated than CO2 CBD extraction. First, plant matter is introduced in a distillation tank. With the use of water and heat, the produced steam carries oils to the top of the tank, and it is then passed through a condenser, resulting in a mix of water and oil. The mix then goes through further distillation to separate water and oil, and the result is full-spectrum CBD oil.
While this CBD extraction process is much simpler, there are some downfalls. It is more prone to error, much less efficient, and may potentially damage part of the essential oil profile of the plant. Due to these reasons, steam distillation is very rarely used to extract CBD nowadays, but many labs still use some type of distillation in the process of isolating CBD from full-spectrum oil.
Solvent extraction
This method is also centuries old and is somewhat of a middle point between CO2 extraction and steam distillation when it comes to complexity and efficiency. It bears many similarities to CO2 extraction, albeit without the advanced methodology that’s behind the "supercritical" part.
In layman's terms, this type of extraction involves mixing plant material with some type of solvent that will carry the essential oils given the right conditions and enough time. Some of the most popular natural solvents are alcohol (ethanol) and natural plant oils (including olive oil), with alcohol being much more efficient in dissolving the plant’s compounds. But due to the higher cost associated with ethanol, many manufacturers choose to go with synthetic solvents (hydrocarbons like butane or hexane), which may end up in lower quality, or even CBD oil that's unfit for consumption if they're not removed properly from the final product.
Solvent extraction is a delicate CBD extraction process and its pros and cons, as well as the consistency of the resulting oil, varies greatly depending on the solvent used. It can be more efficient than steam distillation if performed properly, but it carries a lot of risk and most labs choose CO2 extraction if they can afford it.
How to extract CBD at home
At this point, you may be wondering if there's any way you can extract CBD at the comfort of your own home. The short answer is "yes", but it really depends on how willing you are to do further research. The following is not going to be a real step-by-step guide, but it can serve as a starting point and give you some basic guidelines.
Olive oil extraction
Possibly the simplest way to extract CBD oil, as it only requires some CBD-rich bud, olive oil, and some basic kitchen equipment to ensure a steady supply of heat. If you’ve ever made cannabutter, then technically you have already utilized this method before. The only difference in this case, is that you are using hemp and olive oil—but olive oil can easily be swapped out for the oil or butter of your choice. This includes regular butter, coconut oil, hempseed oil, etc.
The first step for olive oil extraction is decarboxylation, i.e. activation of the compounds of plant material with the use of heat (there’s more info in the following section). Trimmed hemp flower in an oven tray heated between 240 and 280°F (115-135°C) for up to an hour should do the trick. Once this step is taken care of, the resulting activated cannabis is mixed with olive oil and heated at low temperature (ideally in a double boiler) for around two hours. The only thing left to do at this point is to use a filter to strain the mixture and separate the oil from the plant material. The result: CBD-infused olive oil.
While this is the easiest and least risky way to extract CBD oil, it is certainly not the most efficient. As with most DIY projects, there's always room for user error. But even if you do everything right, you are going to sacrifice a large part of the organic compounds of the plant and you will produce less potent oil than a lab would. For these reasons, extracting CBD at home is an interesting experiment, but if you want to reap all the benefits of CBD it is advisable to get it from a reputable source instead.
Activation and purification
While technically not steps of CBD extraction, activation of active organic compounds and purification of CBD oil are two processes that are very important in CBD production. The most common methods used for these purposes are decarboxylation and winterization.
Decarboxylation
The active organic compounds of the cannabis plant come in their acidic forms. In order to go from THCA and CBDA to THC and CBD, manufacturers need to apply heat and decarboxylate the compounds—that's the lab equivalent to lighting up a joint. Heat removes a carbon molecule from the organic compounds and turns them into their active counterparts.
Decarboxylation may take place before or after the extraction, and the exact methodology followed is highly dependent on this choice. But it is an essential part of the CBD oil production process, as non-activated compounds have little to no effect on the user.
Winterization
While not as essential as carboxylation, winterization is a very common process that ensures that the final product of the extraction is as pure as possible. Simply put, the process of winterization employs solvents (usually ethanol) and low temperatures to ensure that lipids and other impurities are removed from an oil extract. This takes place as one of the final steps before full spectrum oil is obtained.
Winterization is not always performed, but it is a very important process when the final product is intended to be vaped. Some terpenes and other compounds are also filtered out during this process, but many manufacturers choose to add terpenes to their CBD oil after winterization.
CBD extraction: the takeaway
These are the most commonly used CBD extraction methods and, as expected, each comes with its own advantages and disadvantages. The main takeaway from this guide should be that the reason you may have seen “supercritical CO2 extraction” in ads and promotions is not just that it sounds cool (although it does!) Simply put, CO2 extraction is by far the cleanest and most efficient CBD extraction method—and a no-brainer for any lab that can actually afford it.
This doesn’t mean that all CO2-extracted CBD products are better by definition. But if a lab invests in the equipment that’s required for the most technically demanding extraction method, chances are that they know what they are doing. When in doubt, check lab tests, and always choose third-party tested CBD products from reputable sources.
President Trump promised during his election campaign to “save vaping," but his administration has undermined that goal at every turn.
The U.S. disposable vape market has grown to $2 billion in annual sales, although nearly none of the products are authorized by the FDA.
More than 30 bills that would impose severe restrictions vaping consumers’ product choices remain active in U.S. state legislatures.
The Freemax REXA PRO and REXA SMART are highly advanced pod vapes, offering seemingly endless features, beautiful touchscreens, and new DUOMAX pods.
The OXVA XLIM Pro 2 DNA is powered by a custom-made Evolv DNA chipset, offering a Replay function and dry hit protection. Read our review to find out more.
The SKE Bar is a 2 mL replaceable pod vape with a 500 mAh battery, a 1.2-ohm mesh coil, and 35 flavors to choose from in 2% nicotine.