Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) is a minor cannabinoid and precursor to delta 9 THC.
Unprocessed THCA doesn’t bind effectively to the endocannabinoid system and won’t produce psychoactive effects. Heat or age, however, converts THCA into intoxicating delta 9 THC. You can still get high from THCA products; just not as high as marijuana, especially with carts.
High heat is generally needed to produce weed oil. Crafting a pure THCA oil is challenging to impossible, so instead, brands dilute it with other cannabinoids.
For a milder high, THCA carts are a cannabis product worth trying out.
What are THCA vape carts?
A THCA vape cartridge is a small, cylindrical tank filled with THCA-rich oil; though the true concentration varies drastically. Oil is housed in a glass chamber, and a built-in atomizer converts the oil to vapor. The atomizer is located at the bottom of the chamber, opposite the mouthpiece.
Never buy a THCA cart without checking the certificate of analysis (COA) first. This is necessary to verify third-party testing, of course, but it also reveals the true amount of THCA in the product. Because these carts are so challenging to produce without converting THCA into delta 9, many contain just trace amounts of the advertised cannabinoid.
Don’t take the marketers’ word for it. Some manufacturers dilute their products with nonintoxicating cannabinoids like CBD, meaning that the product isn’t going to get you very high. If getting high is your goal, delta 8 blends are a better bet.
Keep in mind that vape oil and tinctures are not repackaged versions of the same product. You can’t load a refillable cart with a THCA tincture. Vaping tinctures isn’t safe, and the tincture is usually too thin to work in a cart anyway.
You’ll find THCA vape carts in several sizes. One and two-gram carts are the most common, although some manufacturers offer larger options.
Do THCA carts get you high?
Yes, in most cases, THCA carts will trigger a mild to moderate high.
Since high temperatures convert THCA into THC, vaping it will create psychoactive delta 9 THC. Since oil carts are difficult to produce without THCA becoming THC along the way, manufacturers often blend THCA with other hemp extracts to keep their formula’s delta 9 content under 0.3%.
While reputable hemp sellers use safe-to-ingest cannabinoids like delta 8 to dilute THCA, cost-cutting brands may add fillers. Stay vigilant when shopping for THCA carts. Less reputable companies could even include dangerous additives like vitamin E acetate.The conversion of THCA to THC isn’t one-to-one, either. A THCA molecule is heavier than THC due to the addition of a carboxyl group. Once the group is removed during decarboxylation, you’re left with less THC than whatever quantity of THCA you began with.
Temperatures above 230° F (110° C) will decarboxylate THCA, quickly converting these molecules into psychoactive THC. Standard vaping devices will produce temperatures above this cutoff.
In short, heated THCA can get you almost as high as marijuana, but carts don’t usually contain pure THCA. If it's blended with delta 8 THC, for instance, expect to get high. Mixing THCA with fillers or CBD, however, will further dampen the euphoria.
Are THCA vape carts safe?
Yes, THCA carts are generally safe if they’re purchased from reputable manufacturers with transparent safety testing.
Hemp products of any kind are unregulated. While there’s no formal requirement that brands test for contaminants, this is a key step for any trustworthy manufacturer. Lab testing ensures that the cannabinoid content is accurate and products are safe for human consumption.
To keep a cart’s delta 9 THC content under the legal limit of 0.3%, it’s likely that shadier brands will add fillers to THCA. These could be basically harmless, or they could cause lung irritation or even serious damage. Don’t buy THCA carts without reading the certificate of analysis (COA) first. If the manufacturer can’t show its testing, pass.
The THCA cannabinoid itself is safe to consume. You won’t ingest large amounts of the raw form if you’re vaping it, but unheated THCA may have medicinal benefits.
If you’re sensitive to any popular hemp-derived products, be sure to double-check the THCA cart’s ingredients. Most carts are blends and will contain other cannabinoids, including delta 8 THC.
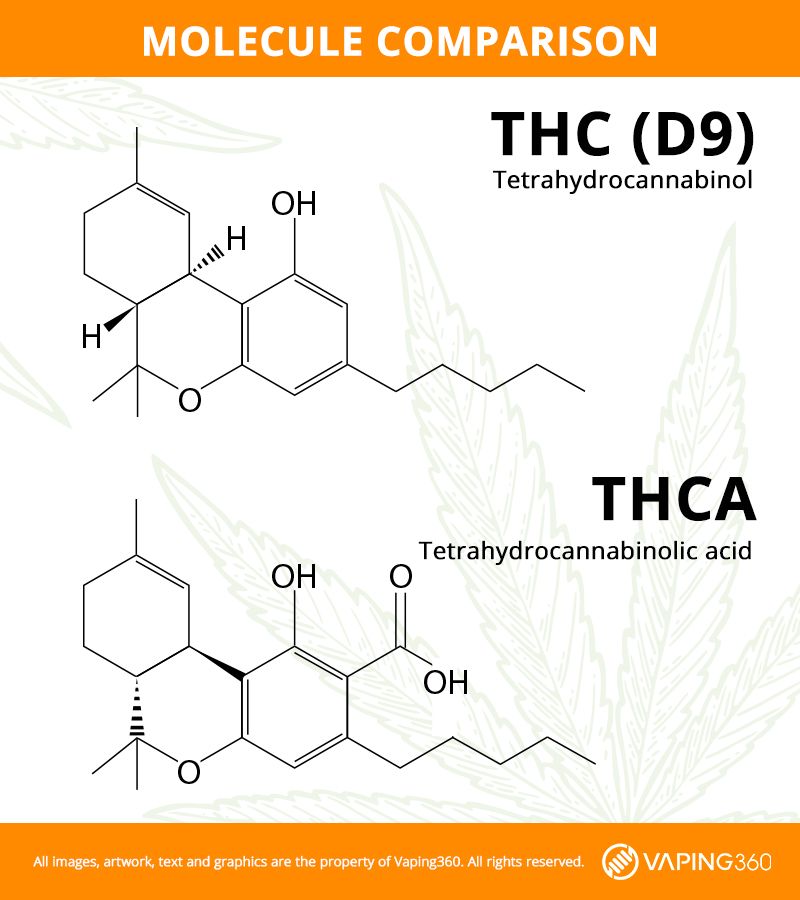
THCA vs delta 9 THC
THCA is the acidic precursor to delta 9 THC. These cannabinoids are almost identical on a molecular level, the key difference being an extra carboxyl group in THCA. Once this feature is removed via decarboxylation, THCA becomes THC.
Exposure to conditions like heat or sunlight speeds up the process. Regardless, the conversion of THCA into THC is a natural part of the cannabis plant’s life cycle, with or without human intervention. It will occur on its own, given enough time.
Even dispensary-bought weed isn’t high in THC at the time of testing or sale. Marijuana contains predominantly THCA before it’s cooked—but, even so, it contains too much delta 9 THC to qualify as hemp.
Consuming raw marijuana flower without applying heat first doesn’t get you high. The plant’s delta 9 THC content is low prior to decarboxylation. You wouldn’t munch on uncooked flower and expect it to hit like an extract—the same applies to high-THCA flower and unprocessed THCA. Both unheated marijuana and hemp are low in delta 9 THC, though hemp contains far less.
Delta 9 THC oil will get you higher than THCA oil or carts. Formulating high-THCA carts without exceeding the 0.3% delta 9 limit is a struggle, but marijuana products aren’t subject to the same restrictions. Even if a marijuana cart contains over 0.3% THC at the time of testing, it’s not an issue.
Unfortunately, this puts THCA manufacturers in a rough spot. The extraction process is enough to convert most THCA in raw flower into delta 9 THC. If a THCA cart contains too much delta 9, it needs to be scrapped and reformulated.
THCA carts vs high-THCA flower
Although THCA flower comes with its own caveats, it’s easier to find than THCA carts or disposables.
Unlike THCA carts, high-THCA flower doesn’t require substantial heat during growth or production, so it tends to keep its THCA intact until sale. Flower is cultivated in tightly regulated conditions to keep its THCA content high, despite being low in delta 9 THC. A colder environment is essential. Overall, this is more tedious than growing standard hemp.
THCA carts are even more complex. In order to produce vape oil, cannabis flower needs to encounter heat. It’s extremely tricky to create THCA carts without decarboxylation occurring during production. Nearly all carts contain a blend of extracts, as these are needed to dilute THCA and keep a cart’s delta 9 THC content below the legal limit.
The medicinal benefits of THCA likely don’t apply to THCA carts. Even if your oil contains 30% THCA, this will convert into delta 9 as you vape it. Raw flower (marijuana or high-THCA hemp) consumption may have anti-inflammatory effects, including irritable bowel disease (IBD) relief. Research also suggests that THCA has neuroprotective qualities. It’s unconventional, but you can add uncooked flower to smoothies or salads.
Both THCA carts and high-THCA flower are difficult to produce. If you want to consume unprocessed THCA for medicinal reasons, flower is preferable.
Are THCA vape carts legal?
Yes, THCA vape carts are legal under the 2018 Farm Bill, although they’re legally nuanced.
Like any hemp-derived vape product, THCA carts are required to contain under 0.3% delta 9 THC by dry weight. Staying within the legal limit isn’t easy. Most hemp cannabinoids, such as CBD, don’t turn into delta 9—at least not naturally. On the other hand, THCA is the immediate precursor to delta 9 THC. It will convert with heat or time.
Marijuana is a federally controlled, Schedule I drug in the United States. Even if you live in a state that allows recreational or medical use, licensed dispensaries are the only legal way to acquire flower, carts, and other marijuana products. You can’t buy them online or from vape shops.
To confirm that a THCA cart is legal, stick to reputable brands and check the COA before purchase. Third-party test results will specify the exact amounts of delta 9 THC and THCA in your product.
How to use THCA vape carts
Broadly speaking, 510 thread carts are simple to use. All you need is the oil-filled cart and a compatible battery or power source.
Before vaping a cart, ensure that the oil is high-quality and hasn’t gone bad. Expired oil is often easy to identify; if the THCA oil is dark brown or black, you shouldn’t vape it. A total lack of air bubbles, or even a cart that’s filled with them, can also indicate poor quality. Watery oil is another giveaway.
THCA vape carts are useless without a power source. Vapers must connect their cart to a battery, since without energy, the coil won’t heat. The vast majority of carts are 510 threaded and compatible with any 510 thread battery. As long as you have a stick or standard vape battery on hand, you’re good to go.
To hook your THCA cart up to a battery, screw it into the threading. Just check that your battery is already charged up and ready to use.
How to choose the right THCA cart
With so many nuances behind its production, choosing the right THCA cart is a process. The contents of THCA carts vary hugely, and some include negligible amounts of the cannabinoid. You’ll even see “THCA carts” containing such small amounts of THCA that laboratories can’t detect it.
Due to the lack of hemp regulations, there’s little that can be done to prevent misleading marketing. It’s up to consumers to double-check COAs and confirm that their cart is genuine.
After confirming that the THCA cart is third-party tested, consider:
- Size: THCA vape carts come in a few sizes. One and two grams are most common, though some companies offer larger carts. Half-gram (500 mg) THCA carts are either rare or nonexistent. If you’re a frequent vaper, you may prefer carts containing two grams of oil or more.
- Blends: It’s typical for brands to mix popular cannabinoids, but this is usually a necessity for THCA. Some THCA blends are more intoxicating than others. If your goal is to get high, try a THCA cart containing delta 8 THC. CBD blends are available for users who want a more subtle experience.
- Potency: This goes hand-in-hand with the previous point. THCA potency varies a lot between carts. We found several THCA carts containing around 40% of the cannabinoid, while others feature far less.
- Terpene profile: The effects and flavor of your cart depend on terpenes. Terpenes are a standard ingredient in any THCA cart, and may be derived from various indica, sativa, or hybrid strains. Indica is preferable for relaxation, while sativa is best for an energizing head high.
For firsthand descriptions of a THCA cart’s quality and effects, check out customer reviews. If you can find feedback outside the company’s website, even better; some review sections are filtered.
Will THCA carts make you fail a drug test?
Yes, it’s wise to avoid all THCA products before a drug test or pre-employment screening—and carts with a low THCA concentration aren’t exceptions to the rule. Ideally, you should steer clear of any cannabis derivatives, including those from hemp.
Screenings aren’t checking if you have delta 9 THC in your body. In actuality, D9 is processed quickly and doesn’t stick around in the user’s system. Drug testers are actually looking for the THC-COOH metabolite, which is produced by the liver after metabolization. There’s no way to determine whether THC-COOH came from hemp or marijuana.
THC-COOH lingers in fat for some time after your last use, though traces may also be found in hair and nail cells. Chronic vapers can require up to three months to fully clear this breakdown product from their systems. Less frequent users likely won’t need more than a month, but the longer you abstain, the better.
Most derivatives of psychoactive hemp convert into THC-COOH, even if they don’t become delta 9 prior to consumption. Potential exceptions exist, such as HHC, but it’s highly inadvisable to consume them before testing. Playing it safe can prevent avoidable trouble.
THCA is even more of a black-and-white situation. When you vape a THCA cart, you’re consuming delta 9 THC, not a typical hemp cannabinoid. Your metabolism will treat THCA products identically to those containing THC. And that’s bad news if you’re taking a drug test anytime soon.
The Freemax REXA PRO and REXA SMART are highly advanced pod vapes, offering seemingly endless features, beautiful touchscreens, and new DUOMAX pods.
The OXVA XLIM Pro 2 DNA is powered by a custom-made Evolv DNA chipset, offering a Replay function and dry hit protection. Read our review to find out more.
The SKE Bar is a 2 mL replaceable pod vape with a 500 mAh battery, a 1.2-ohm mesh coil, and 35 flavors to choose from in 2% nicotine.
Because of declining cigarette sales, state governments in the U.S. and countries around the world are looking to vapor products as a new source of tax revenue.
The legal age to buy e-cigarettes and other vaping products varies around the world. The United States recently changed the legal minimum sales age to 21.
A list of vaping product flavor bans and online sales bans in the United States, and sales and possession bans in other countries.
Find Your Perfect Product
Navigate our vape database precisely by customizing your filters. Find products tailored to your needs with options like price, category, and more.
Sort by:
Empowering Vapers Worldwide
As a recognized authority in the vaping world, Vaping360 draws over a million monthly visitors to read our in-depth reviews and guides, breaking news, and insights on the latest vaping products and events impacting the vaping world. Our mission is to achieve a healthier, smoke-free world.