CBD is a compound found in cannabis plants that has a variety of known health benefits—notably the ability to relax and soothe the user. Unlike its cannabinoid relative THC, the effects of CBD (which is short for cannabidiol) are produced without intoxication. CBD is psychoactive—it reduces anxiety—but it doesn’t create a “high” like THC does.
Hemp has been cultivated for thousands of years for its fiber, and more recently as a source of CBD. The 2018 Farm Bill that legalized industrial hemp production in the U.S. pushed the already growing CBD industry into overdrive, and now CBD is legally available in most places in the country—as long as it contains less than 0.3% THC. Hemp-derived CBD doesn’t usually contain measurable amounts of THC.
CBD is extracted from industrial hemp or marijuana plants (both are cannabis) and processed for several methods of consumption. Vaping is the fastest way to experience the effects of CBD, because inhalation delivers your preferred CBD dose to the bloodstream and brain much more rapidly than other methods.
In addition to being absorbed more quickly, inhalation provides greater bioavailability, which means you can absorb more CBD from the same quantity than you would using other methods. While there is still more to learn about the long-term effects of vaping CBD, vaping is considered to be much safer than smoking, while being equally effective.
CBD e-liquid is sometimes called CBD oil, but it contains no actual oil, which can be dangerous to inhale. Like all e-liquid, CBD vape juice contains vegetable glycerin (VG) and propylene glycol (PG). But CBD tinctures and edible products contain actual oils, which are perfectly safe to swallow. (You can use CBD vape juice orally too, if you prefer.)
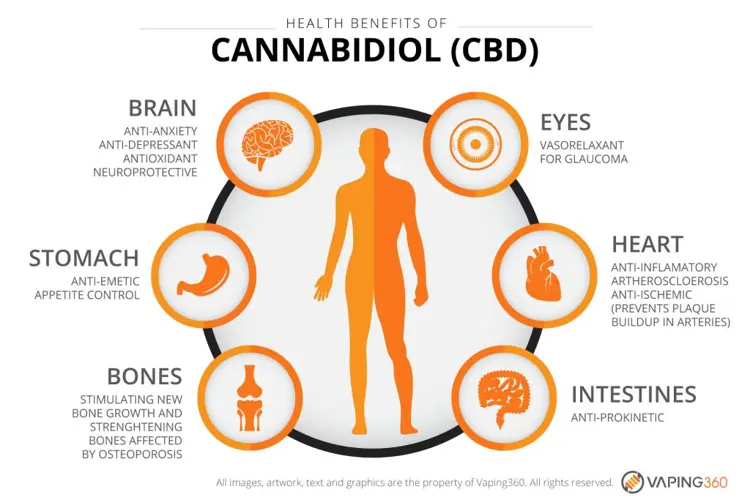
There is considerable research suggesting that cannabidiol produces positive effects that can treat a variety of conditions and symptoms. In this guide, we look at the most well-documented effects and benefits of using CBD oil.
What are the effects of CBD?
The most commonly reported effects of CBD are a sense of calm or relaxation, relief from pain or anxiety, and an overall improvement in mood. In high doses, CBD can induce drowsiness or sleep, but in small amounts, it can actually have the opposite effect, promoting alertness. These are the effects most CBD users seek:
- Relaxation or calmness
- Reduced anxiety and stress
- Improved mood
- Comfort
- Pain relief
- Sleepiness (in high doses)
- Alertness (in low doses)
CBD oil made from hemp typically doesn’t contain enough THC to get you high, but it can produce a strong sense of calm without the uneasiness, paranoia and other side effects some people experience from marijuana. That’s actually why a lot of people use CBD. Many users specifically take CBD oil for anxiety.
But there’s a caveat: the speed and intensity of these effects depend on how it’s consumed. The effects of vaping CBD come on faster. Even though the sensations will eventually be generally the same, a CBD oil tincture, or a CBD edible will take longer, and will probably require more CBD content to deliver the same benefits.
These are the most common ways of using CBD, listed from the fastest delivery to the brain and body to the slowest:
- Vaping in a mod with CBD vape juice, or using CBD oil pens or cartridges
- Vaping or smoking CBD-rich hemp flower or high-CBD cannabis strains
- Using CBD oil tinctures sublingually (under the tongue)
- Wearing a CBD transdermal patch
- Eating CBD gummies or edibles
- Swallowing CBD capsules or pills
- Using CBD creams or topicals
One last thing to remember is that the faster you absorb and process CBD, the more quickly it leaves your system. Vaping is the quickest way to feel the effects of CBD, and it’s also the quickest to process through your body. Edibles or other products that are processed through the liver and digestive system linger in your body for a longer time.
What are the benefits of CBD?
Scientific research suggests that CBD has a wide range of therapeutic properties. Here are some of the benefits and potential benefits studies show that CBD may provide for a variety of conditions.
Epilepsy and seizure disorders
As far back as 1973, research showed that CBD actively reduced or blocked convulsions in rodents, which was confirmed by other studies soon after. In later research, epileptic patients that received 200-300 mg of CBD per day had fewer seizures.
One of the most well-documented examples of CBD as an anti-convulsant was a young girl named Charlotte Figi who suffered from Dravet syndrome, a rare condition that conventional medication was unable to treat effectively. She was given a tincture derived from a low-THC/high-CBD cannabis strain, which was later named Charlotte’s Web in tribute to the young patient. Charlotte’s seizures were drastically reduced—from about 1,200 a month to just two or three.
In June 2018 the FDA approved Epidiolex, a CBD-based drug for treating Dravet and Lennox-Gastaut syndromes in patients two and older. Epidiolex is the first drug to gain FDA approval that contains a purified substance derived from cannabis. In April 2020, the Drug Enforcement Administration removed Epidiolex from the controlled substances list, making it much easier for doctors to prescribe the drug to epileptic patients.
Insomnia
One of the most common effects of vaping CBD oil is drowsiness, especially when administered in higher doses. An animal study conducted in the early 1970s first showed the sleep-inducing effects of CBD. In people with insomnia, CBD has been shown to increase sleep time when taken in a dose of about 160 mg. In non-insomnia patients, a similar effect was observed at much higher doses. In micro doses, CBD may promote alertness, instead of inducing drowsiness.
Anxiety
Multiple studies have shown that CBD can effectively treat anxiety. Research using advanced brain imaging has confirmed the anxiolytic effect of CBD. These mood-regulating effects of cannabidiol may also be used to treat depression. Researchers believe that CBD also has the potential to treat other anxiety disorders such as OCD and PTSD.
Psychosis
A 1982 study showed that CBD seemed to inhibit THC-induced symptoms associated with psychosis. Another study from the same year suggested a variety of neural pathways by which CBD might treat psychosis. Researchers believe that CBD can also be used to treat depression and other psychiatric disorders.
Heart disease
CBD is cardioprotective, showing a “tissue sparing effect” during chronic myocardial ischemia and reperfusion. British researchers have also shown that cannabidiol reduced the number of ischemia-induced arrhythmias in rats when given prior to ischemias. This research could prove beneficial to cardiovascular disease patients.
Diabetes
Israeli researchers believe that CBD’s anti-inflammatory properties could prove beneficial for treating type 2 diabetes. Because chronic inflammation can lead to insulin resistance, treatment of inflammation with CBD could improve metabolism and ward off diabetes. The scientists believe that the actions of CBD in the body could also be modified to work on other receptors, and that the compound might be used to treat other diseases caused or worsened by chronic inflammation.
Side effects from chemotherapy
THC has long been accepted as a therapy for nausea induced by cancer treatment. Marinol, a synthetic THC drug, has been approved for that purpose since 1985, and THC in various forms has been widely prescribed to cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. But CBD may also serve as an equally effective treatment for nausea.
CBD interacts with receptors that release the neurotransmitter serotonin, which is partially responsible for causing nausea. In small doses, CBD can help reduce the symptoms of nausea. And an acidic form of CBD called CBDA may be an even more effective anti-nausea drug than CBD or THC, based on early animal studies.
Anti-oxidative and neuroprotective effects
CBD appears to have antioxidant and neuroprotective effects that are unrelated to the cannabinoid receptors. A 1998 study from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke—a rare federally funded study on a Schedule 1 drug—found that CBD “may be a potentially useful therapeutic agent for the treatment of oxidative neurological disorders such as cerebral ischemia” (an artery blockage that can lead to strokes). CBD also shows promise as a therapy for neurological diseases like Parkinson’s.
Should you vape CBD oil?
CBD shows huge potential for treating a variety of medical conditions and diseases, and researchers have barely scratched the surface. When federal legalization of cannabis comes, research funding will open the floodgates, and scientists will begin to explore thousands of therapeutic possibilities for CBD and other cannabinoids.
But until then, many people have found that the currently known benefits of CBD can help them live better lives. If you decide CBD is right for you, there are many ways to use it—not just vaping, but also tinctures, and topical and edible CBD products.
President Trump promised during his election campaign to “save vaping," but his administration has undermined that goal at every turn.
The U.S. disposable vape market has grown to $2 billion in annual sales, although nearly none of the products are authorized by the FDA.
More than 30 bills that would impose severe restrictions vaping consumers’ product choices remain active in U.S. state legislatures.
The Freemax REXA PRO and REXA SMART are highly advanced pod vapes, offering seemingly endless features, beautiful touchscreens, and new DUOMAX pods.
The OXVA XLIM Pro 2 DNA is powered by a custom-made Evolv DNA chipset, offering a Replay function and dry hit protection. Read our review to find out more.
The SKE Bar is a 2 mL replaceable pod vape with a 500 mAh battery, a 1.2-ohm mesh coil, and 35 flavors to choose from in 2% nicotine.